稍微聊聊ECS架构并简单罗一下Unity中的ECS的几个步骤
ECS简介
- Entity(实体):表示一个游戏对象,它拥有一个Component的集合
- Component(组件):表示一个属性的数据部分,通常其中不包含实例方法,但会包含
get,set以及常用的内部数据操作(比如扣血) - System(系统):表示一个属性的行为部分,循环执行Entity的逻辑(例如在onUpdate方法下循环检查敌人是否死亡)
ECS遵循组合优于继承,在Unity中,与传统OOP(面向对象)不同,ECS在代码编写的逻辑上体现为需要什么加什么,让本身拖拽一个个MonoBehavior进对象的操作变成了使用代码动态生成(虽然本身也可以代码拉进来),而数据和逻辑分开降低了耦合,且一般Component和System一一对应则在一定程度上避免了编写代码时逻辑混乱。同时组合这个操作在一定程度上使得其拓展要比传统OOP更为简单且少出错。
ECS与建造者模式类比
ECS和设计模式中的建造者模式(Builder Pattern)非常相似,主要体现于建造者模式的设计初衷为难以使用先有的逻辑以应对变化的需求,于是通过对操作的组合与顺序控制从而生产产品。
如果对ECS感觉比较难以理解,其实可以先去了解建造者模式。
ECS 优缺点
ECS在代码编写时前期相对繁琐,需要大量的组合操作才将对应的逻辑挂载到实体上,意味着需要大量的Spawner来初始化实体,对于整体的开发来说,还是需要思考其是否适用于项目(如果实体很少就不太适用,实体很多都得写spawner)。同时因为需要大量的Spawner,对于在整个游戏中类比较多的情况可能显得不太划算,尤其是在一个实体仅需一个类就能完成所有操作(例如View)的情况下,ECS的优势也较难体现出来。(可参考建造者模式将Spawner封装进Director类里)
ECS最大的优势在于性能,由于实体的数据都存放于Component,其在内存中的结构就像数据库中一样,这样也就极大地增加了CPU缓存命中,在多实体的场景下性能远超传统框架。
总而言之,在多实体且可能实体多行为的游戏内,ECS能够有较大的优势,无论是在性能还是代码的编写上。
一定程度上讲,ECS回到了面向过程而非面向对象,关注于实体拥有何种能力,从而在运行时执行何种行为;而面向对象继承、封装、多态的思想,则被ECS以拆分、组合的操作来达到对应的一个设计目的(清晰的系统逻辑与代码复用等)。二者很难说出孰优孰劣,而是有其对应的场景,ECS要将能力组合,其实在写逻辑时去思考如何去写合理,反而可能导致在功能实现上造成一定的难度,而OOP在写的时候虽然爽,但是后期扩展和维护也有对应的难处。
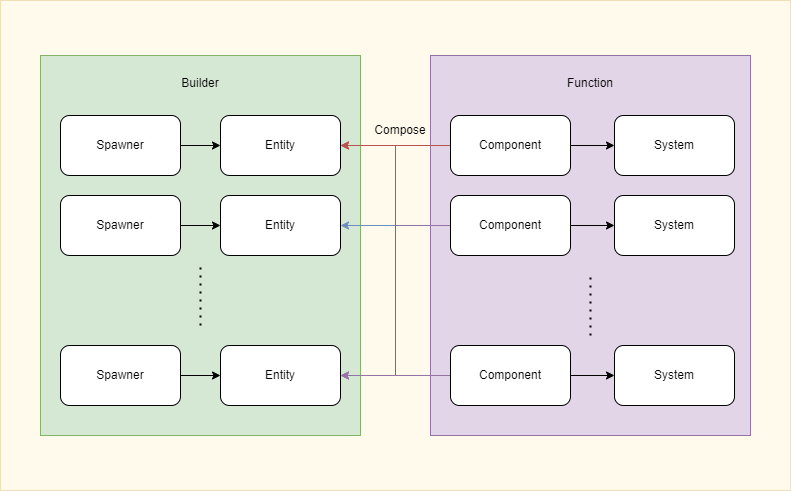
ECS实践示意
主要由两部分组成,构造,行为:
-
构造:通过Spawner生成Entity并挂载Component与初始化参数
-
行为:System会找到有对应Component的Entity并执行行为
ECS实践详细步骤
以下内容参考官方示例
Spawner example | Entities | 1.2.4 (unity3d.com)
插件安装
在Package Manager中Unity Registry下安装以下包体:
选装以下
- Unity Physics: 更好的物理
- Havok Physics for Unity: 要专业版
- Netcode for Entities: 网络
- Entities Graphics: 使用SRP (最新版本请尽量保证使用URP+Entities Graphics,SRP的使用目前我也没跑通)
新建子场景
在Hirerachy窗口中右键New Sub Scene->Empty Scene,并保存
构造
Component数据
新建继承IComponentData的CubeSpawnerComponent,由于Component不是继承自MonoBehavior,我们还需要其他的方法挂载它
using Unity.Entities;
using Unity.Mathematics;
public struct CubeSpawnerComponent : IComponentData
{
public Entity prefab;
public float3 spawnPos;
public float nextSpawnTime;
public float spawnRate;
}Spawner生成Entity
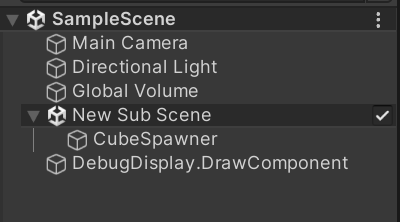
创建类SpawnerAuthoring,其会调用Bake方法新建一个实体并将CubeSpawnerComponent挂载到实体上,这时候运行场景会看到场景中出现了Spawner,记得给Spawner设置Prefab,此处使用方块
using Unity.Entities;
using UnityEngine;
public class CubeSpanwerAuthoring : MonoBehaviour
{
public GameObject prefab;
public float spawnRate;
}
public class CubeSpawnBaker: Baker<CubeSpanwerAuthoring>
{
public override void Bake(CubeSpanwerAuthoring authoring)
{
Entity entity = GetEntity(TransformUsageFlags.None);
AddComponent(entity, new CubeSpawnerComponent
{
prefab = GetEntity(authoring.prefab, TransformUsageFlags.Dynamic),
spawnPos = authoring.transform.position,
spawnRate = authoring.spawnRate,
nextSpawnTime = 0f,
});
}
}System挂载Component并执行行为
接下来是根据Component中的数据执行Entity的行为,继承自ISystem的代码不需要挂载在任何实体上也可以直接运行,在onUpdate方法中编写Spawner的生成逻辑
using Unity.Burst;
using Unity.Collections;
using Unity.Entities;
using Unity.Mathematics;
[BurstCompile]
public partial struct CubeSpawnerSystem : ISystem
{
[BurstCompile]
public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state)
{
if (!SystemAPI.TryGetSingletonEntity<CubeSpawnerComponent>(out Entity spawnerEntity))
{
return;
}
RefRW<CubeSpawnerComponent> spawner = SystemAPI.GetComponentRW<CubeSpawnerComponent>(spawnerEntity);
// 可以直接使用以下方法来创建实体,也可以在Buffer中创建性能
//state.EntityManager.CreateEntity();
EntityCommandBuffer ecb = new EntityCommandBuffer(Allocator.Temp);
if (spawner.ValueRO.nextSpawnTime < SystemAPI.Time.ElapsedTime)
{
Entity cubeEntity = ecb.Instantiate(spawner.ValueRO.prefab);
spawner.ValueRW.nextSpawnTime = (float)SystemAPI.Time.ElapsedTime + spawner.ValueRO.spawnRate;
ecb.Playback(state.EntityManager);
}
}
}这时候运行场景,在Entity Hierachy可以看到对应的prefab不断地在世界中被创建出来
行为
方块会往一个方向往前移动并慢慢减速到0
Componet
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Unity.Entities;
using Unity.Mathematics;
using UnityEngine;
public struct CubeComponent : IComponentData
{
public float3 moveDir;
public float moveSpd;
}System
查找是否有CubeComponent,有则执行
using Unity.Collections;
using Unity.Entities;
using Unity.Transforms;
[UpdateInGroup(typeof(FixedStepSimulationSystemGroup))]
public partial struct CubeSystem: ISystem
{
public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state)
{
var entityManager = state.EntityManager;
var entities = entityManager.GetAllEntities(Allocator.Temp);
foreach(var e in entities)
{
if (entityManager.HasComponent<CubeComponent>(e))
{
var cube = entityManager.GetComponentData<CubeComponent>(e);
var localTransform = entityManager.GetComponentData<LocalTransform>(e);
var moveDist = cube.moveDir * cube.moveSpd * SystemAPI.Time.DeltaTime;
localTransform.Position += moveDist;
entityManager.SetComponentData<LocalTransform>(e, localTransform);
if (cube.moveSpd > 0) cube.moveSpd -= 2f * SystemAPI.Time.DeltaTime;
else cube.moveSpd = 0;
entityManager.SetComponentData<CubeComponent>(e, cube);
}
}
}
}随机运动
在原先的SpawnerSystem中,生成entity后挂载Component并设置参数(随机数的写法会有点奇怪是要传入一个index)
if (spawner.ValueRO.nextSpawnTime < SystemAPI.Time.ElapsedTime)
{
Entity cubeEntity = ecb.Instantiate(spawner.ValueRO.prefab);
ecb.AddComponent(cubeEntity, new CubeComponent { moveDir =
Random.CreateFromIndex((uint)(SystemAPI.Time.ElapsedTime / SystemAPI.Time.DeltaTime)).NextFloat3(), moveSpd = 10f });
spawner.ValueRW.nextSpawnTime = (float)SystemAPI.Time.ElapsedTime + spawner.ValueRO.spawnRate;
ecb.Playback(state.EntityManager);
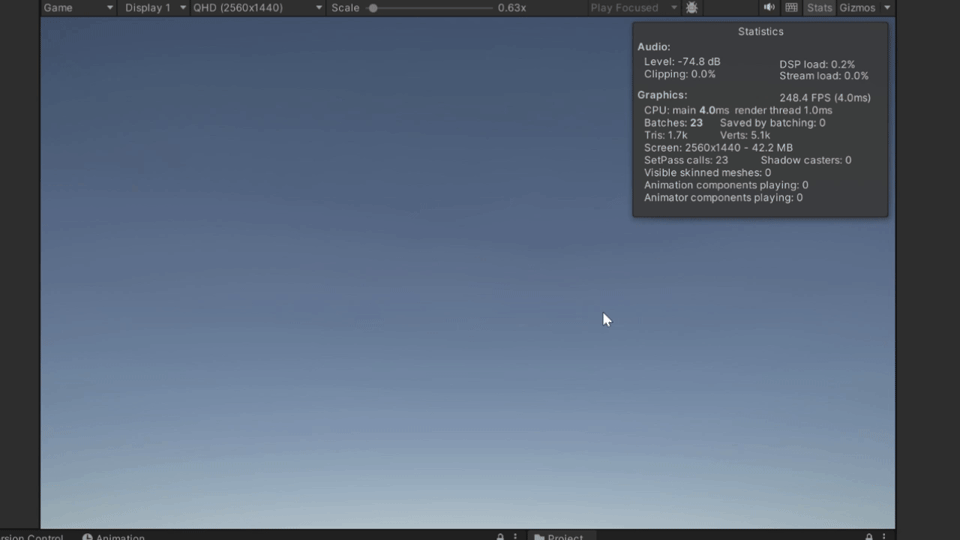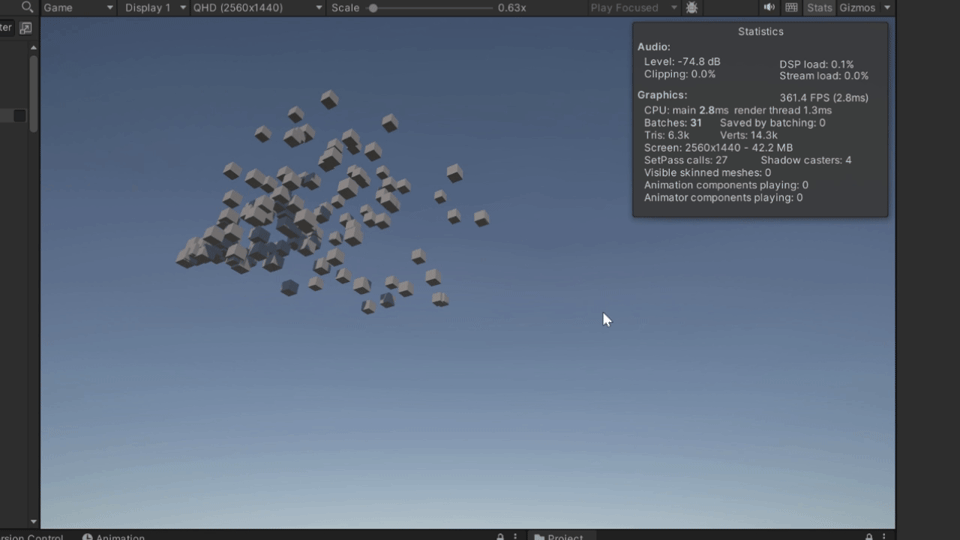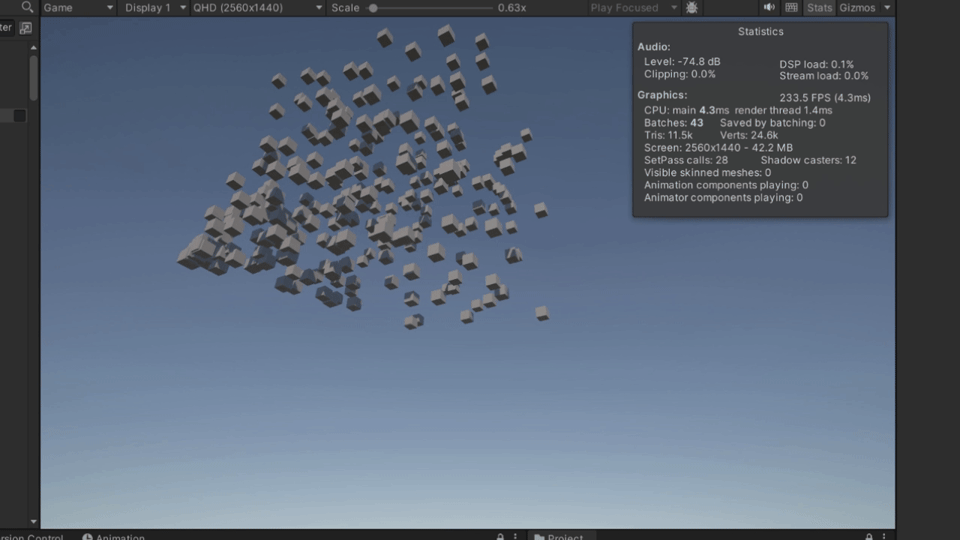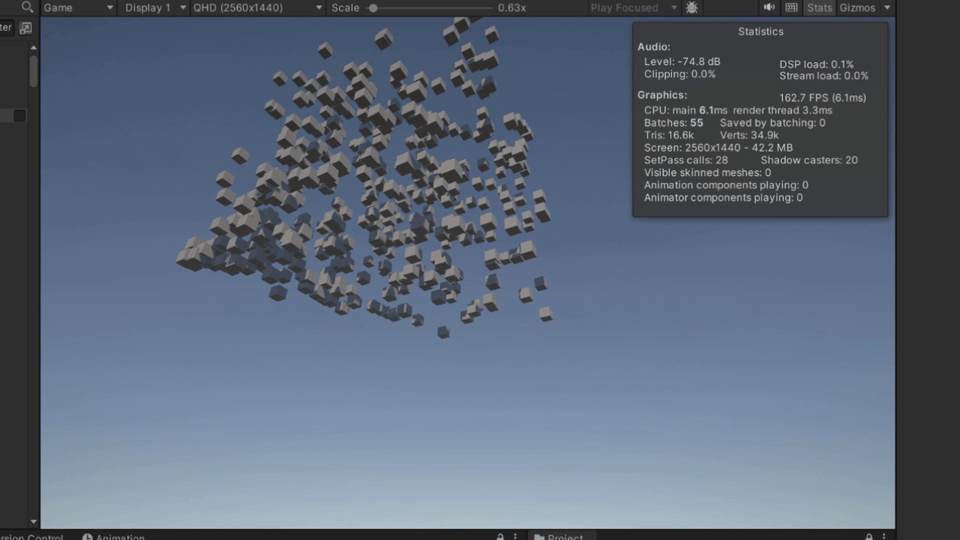
}最后示例如下
报错说明与解决方法
-
Null Reference Exception
NullReferenceException: Object reference not set to an instance of an object Unity.Entities.Editor.HierarchyWindow.OnCleanup () (at ./Library/PackageCache/com.unity.entities@1.0.16/Unity.Entities.Editor/Hierarchy/HierarchyWindow.cs:113) Unity.Entities.Editor.DOTSEditorWindow.OnDisable () (at ./Library/PackageCache/com.unity.entities@1.0.16/Unity.Entities.Editor/Common/DOTSEditorWindow.cs:201)关闭编辑器中的Hirerachy窗口即可,可以不管
-
Entities.Graphics should be used with URP Forward+.
找到项目使用渲染品质对应的URP-quality-Renderer,将
Rendering Path改为forward+
